ENERGY AND VITALITY
“Stress and fatigue lead to addictive behaviors.
This vicious circle must be broken step by step.”
Dr Roth, Thomas
Causes of Lack of Energy
Lack of energy is basically a cell damage or a disorder of the cell. It loses the ability to provide the necessary energy. The mitochondria (the power plants of the cell) are at the center of energy production. Many therapeutic measures (see below) aim to reactivate or strengthen the mitochondria; a more detailed explanation of these complex molecular biological and electrophysiological processes would be too long; two aspects are described under ATP and pH value.
Chronic stress (see stress medicine) is one of the causes of tiredness and lack of energy, but there are others:
- The diet is oriented towards fast foods (fast food, sandwiches, etc.) and becomes rich in carbohydrates and sugars, which makes us tired (brain fog).
- Chronic overacidification of the body leads to a loss of energy over time.
- Preservatives and bad carbohydrates damage our intestines, causing malnutrition (micronutrient deficiency) with possible neurological disorders over time.
- Last but not least, there is the sad topic of numerous toxins to which we are inevitably exposed. They accumulate in our body (especially in adipose tissue) and cause a latent chronic inflammation, not immediately recognizable, which can then lead to numerous symptoms.
- For completeness, we should also mention invisible electrosmog (electromagnetic waves such as those from smartphones, radiation from antennas, microwaves, etc.), which inhibit our detoxification processes and can even cause tumors in the medium and long term. Young children and adolescents are particularly vulnerable.
All of this leads to fatigue and energy deficiency. Understandably, we try to compensate for this condition. But this is where the vicious cycle begins, as it is compensated by quickly available energies: coffee, cigarettes, stimulants, and even drugs. Or we seek other distractions or compensations, such as social media, Netflix, shopping, excessive sports, or movies. In the evening, we have difficulty relaxing, so alcohol and/or sleeping pills are consumed, which may provide short-term subjective (mental) relaxation, but unfortunately add additional stress to our brain and body, generating a boomerang effect.
Remedies and measures to increase energy
To stay healthy, the body must be able to regenerate. Regeneration mainly occurs at night and especially only when the parasympathetic nervous system is activated (relaxation mode, as opposed to sympathetic mode = stress). It is therefore essential to be able to relax, or at least to try. As simple as this may seem, it can sometimes be difficult in a busy daily life. However, it is possible with consistent daily training, for example, by taking short breaks, energy naps (= short naps (maximum 30 minutes) during lunch breaks), and breathing exercises (1 to 2 minutes) several times a day, especially during a stressful day.
- Micronutrients
- Modification of the diet
- Physical exercise (30 minutes, with a heart rate of about 120; a minimum of 10,000 steps per day, which corresponds to more or less 1 hour of walking)
- Stress reduction (work-life balance)
- Behavioral therapy (in collaboration with a coach or specialist)
- Reduction of exposure to harmful substances
- Smoking, alcohol, cosmetics, perfumes, chemicals, drugs, …
- Pollutants in the workplace
- Water filter (heavy metals, hormones, etc.)
- Quality of sleep (sleep disorders)
- Intestinal treatments
- Detox and metabolic treatments
- Oxidative therapies
- Sauna
- Cold baths, Kneipp therapies
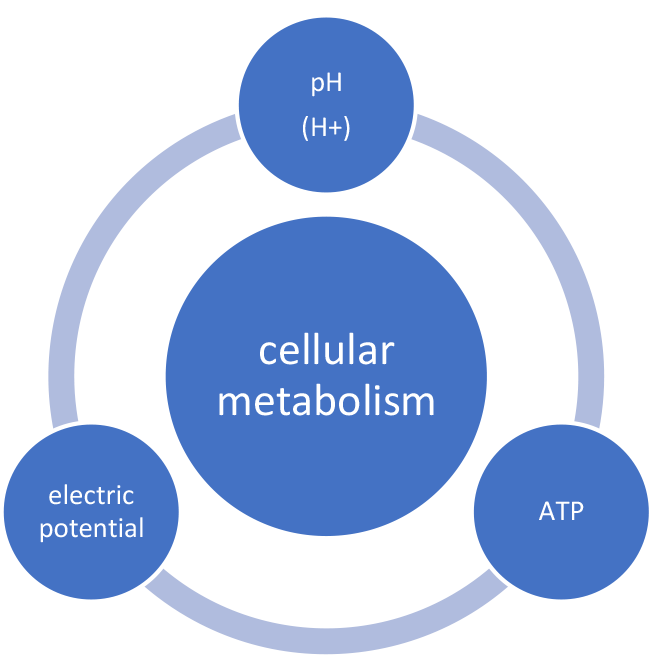
ATP and pH value
There are two important elements that are directly related to each other and are essential for energy production:
ATP (= adenosine triphosphate)
- In the cell, it is an energy carrier.
- Outside the cell, however, it is a signaling molecule that triggers an immune response. This in turn leads to oxidative stress, which primarily serves to protect the cell and kill bacteria. If the surrounding cells are unable to compensate for the damage, the immune response and the ongoing oxidative reaction lead to symptoms and, over time, disease.
Hydrogen ion (= proton = H+)
- Hydrogen is a central element in the cell’s energy production.
- It is responsible for the pH value (Latin: potentia hydrogeni which means hydrogen potential). As it has a positive charge, it also has an effect on the electrical potential of the cell and its membranes. The pH and electrical potential regulate various intracellular processes; the alteration of pH and electrical potential disturbs the intracellular homeostasis and can subsequently lead to the accumulation of substances that “poison” the cell and even inhibit energy production. The aim of the above-mentioned measures is to break this vicious circle step by step and restore the natural balance. This regeneration process can last months and, in severe cases, even years.